The Windows Startup folder is located at C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
Actually, there are two start up folders in Windows 10 and 11, the first one (the one noted above) is the Current Users folder. The other is called the All Users Startup folder is located here C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp
What Are Current User & All Users Windows Startup Folders?
The Current User startup folder is specific to an individual account (or user). Each user, or user account, on your computer has its own startup folder and items placed within it will only affect that user account.
Whereas the All User startup folder is a system wide folder. Anything inside this folder will start whenever the computer is booted up, regardless of which user account is logged into.
How To Access The Windows Startup Folders.
To open the Windows Current User Startup folder, either navigate to C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup where Username is the name of the account you’re trying to access.
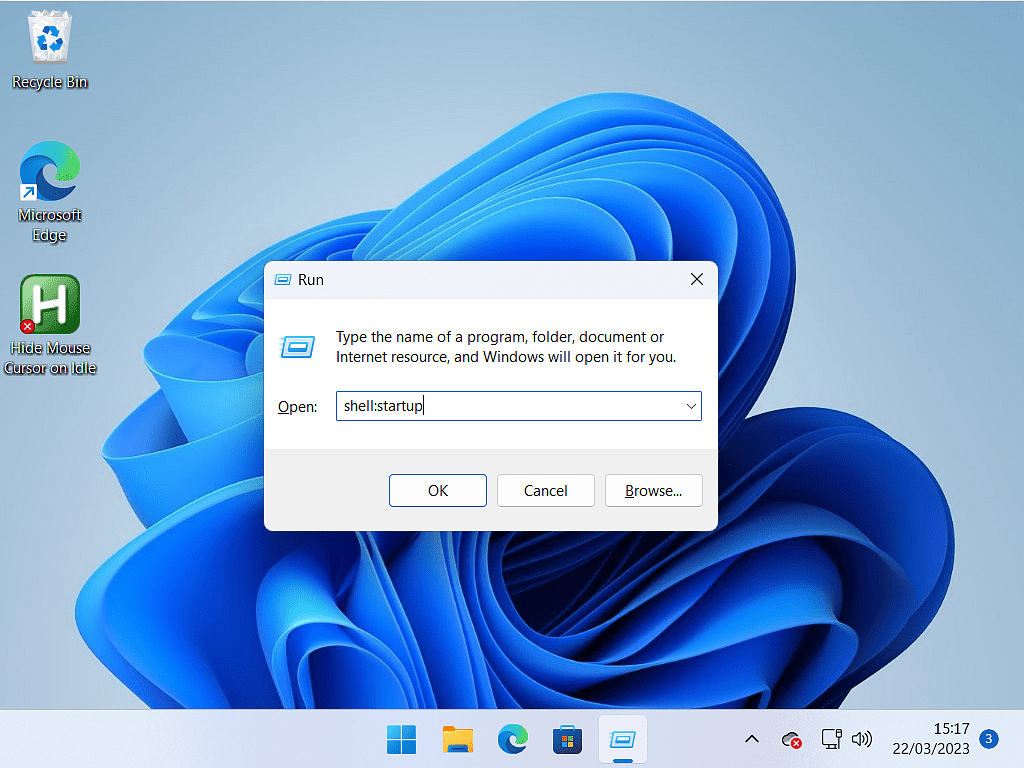
Or open the Run box (Windows key and the letter R) and type shell:startup
And to access the Windows All Users Startup folder, navigate to C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp.
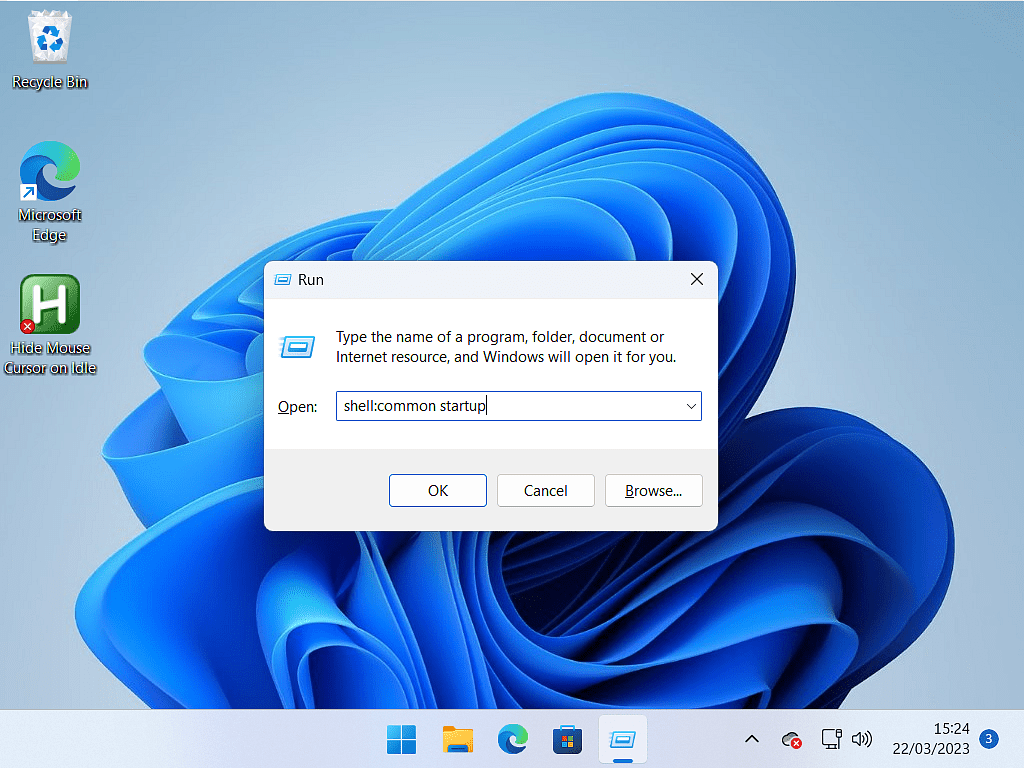
Or enter shell:common startup into the Run box.
Adding And Removing Items In Windows StartUp Folder.
Generally speaking, you can remove any items from the Startup folders that you don’t want to launch every time Windows boots up. Since most of the items will be shortcuts, they can usually just be deleted.
Similarly, you can add items that you do want to launch with Windows. To add an item, simply create a shortcut and then copy the shortcut into the startup folder. You don’t normally add the exe file, but rather the shortcut to the exe file.
For Example.
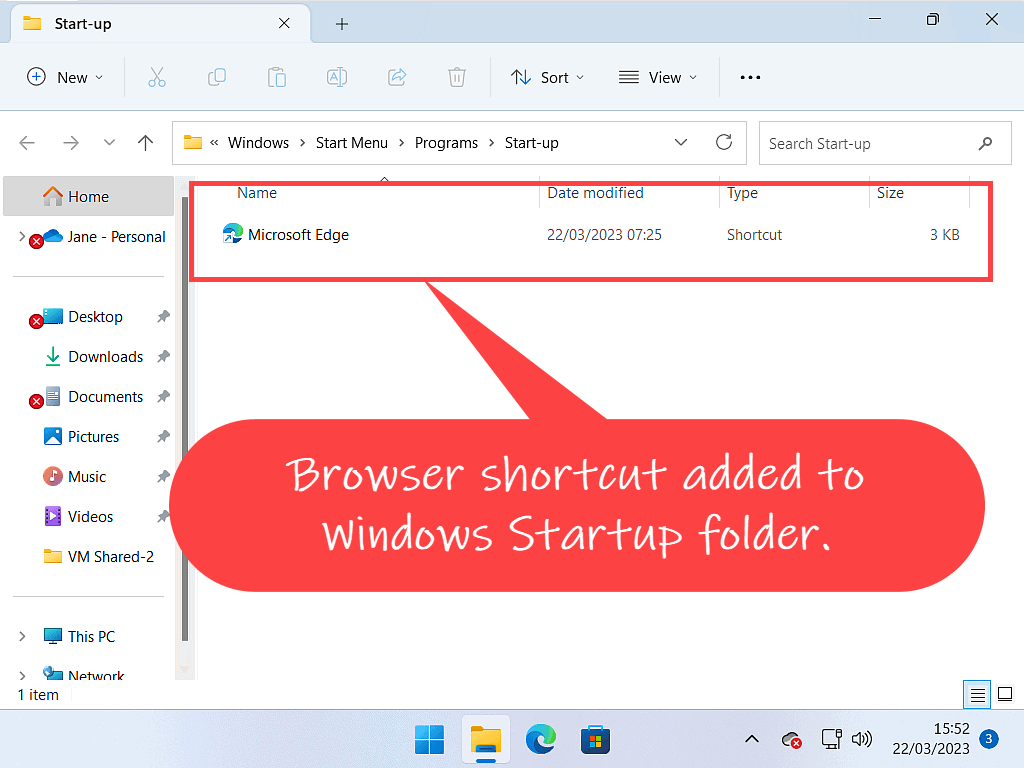
As an example, let’s say you wanted your web browser to open each and every time you started your computer. Simply copy and paste the browser shortcut into the Windows Startup folder. After doing that, your browser will automatically open when Windows starts.
Later, if you change your mind, just re-open the startup folder and delete the shortcut to stop it automatically opening with Windows.
Startup Folder Launch Order In Windows 10 & 11.
When Windows 10 and 11 boot up, they launch programs/apps in a very specific order. Necessary system processes and (fairly obviously) the first to start. After that comes any items in the Task Manager Startup tab and finally comes the items inside the Windows Startup folder.
In practice, that means you will have to wait a short while before your program/app opens, but on modern machines, that’s not usually too long.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that having too many items inside the startup folder will slow down your computer’s boot time. So if you’re adding programs to the folder, be selective. Only put in there what you really do need straight away.